ONNX-opt 0
今天是人类目前最大的湿件制导导弹命中目标的24(man!)周年
ONNX 简介
ONNX 是一个开放的深度学习框架中立的表示格式,旨在促进不同深度学习工具之间的互操作性。通过 ONNX,开发者可以在不同的深度学习框架之间轻松地转换模型,从而实现更高效的模型部署和推理。
ONNX 和 ONNX-runtime 是两个重要的组成部分,前者是模型计算图和权重的中间表示,后者是一个推理引擎,如下图。
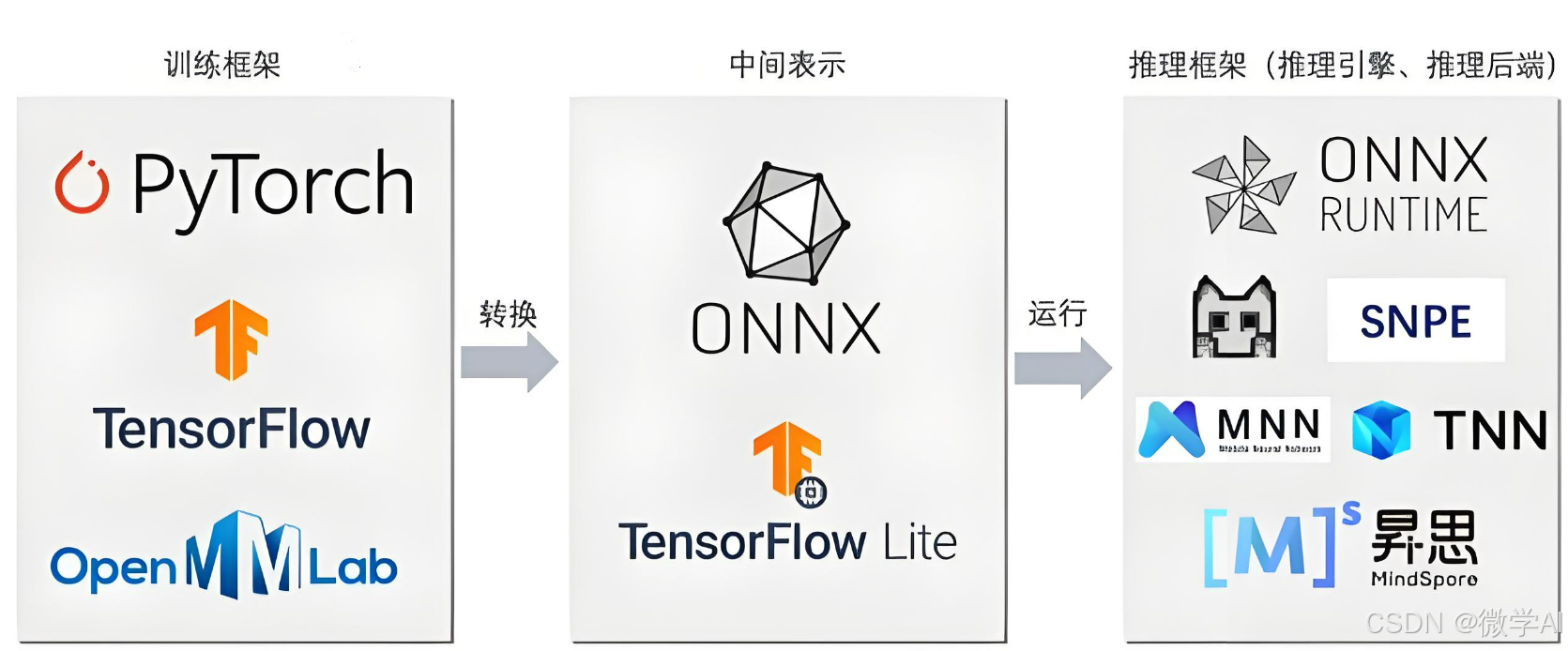
所以 ONNX 主要用于 AI 模型的交换和部署:
- 交换:对不同训练框架导出模型文件和权重文件进行转换
- 部署:将模型文件和权重文件交给推理引擎进行运算
上图中的三段式和传统编译器的结构不谋而和,ONNX 虽然并不存在计算图或者算子上的简化,但是其中的一些结构对于模型的抽象使得优化其实不是完全不可能(进入编译器舒适区间了)
比如,现在已有的 ONNX-simplifier(虽然不是很流行),根据其描述是进行计算图上的常量折叠,以及他的third-part依赖ONNX-optimizer
相较于如何优化这方面,也很重要的方面是如何对 Pass 后的结果进行验证,下面是一些主流的 AI 编译器的测试方法(gen by Gemini)
| 框架/标准 | 主要验证策略 | 核心工具/方法 |
|---|---|---|
| ONNX | 结构合法性验证、数值一致性对比 | onnx.checker、ONNX Runtime(对比不同优化级别/后端)、模型库测试 |
| MLIR | 逐层方言规约验证、Pass正确性断言 | Dialect Verifier、mlir-opt + FileCheck、端到端数值对比 |
| TVM | 端到端数值对比、中间层IR对比、底层代码单元测试 | Relay解释器(对比优化前后)、与NumPy对比、端到端与原始框架对比 |
| Triton | 与参考实现的数值一致性对比、梯度检查 | 与PyTorch Eager实现的输出对比、torch.autograd.gradcheck进行梯度验证 |
相比之下,ONNX 有一些优势,提供了足够的语法与结构规约验证(Syntactic and Structural Verification)的 Python API,不必一定要进行数值一致性对比 (Numerical Consistency Check), 虽然后者可以通过 ONNX Runtime 来实现
不过数值一致性对比还是很有必要的,但是对规模比较大的测例而言,算力也是一个问题
ONNX 的另一个优点在于,它不像是 TVM 进行端到端的训练和部署,所以研究性的工作可能会比轻松
ONNX 环境配置
由于是进行研究,所以需要一套源代码 ONNX 1.19.0 release
再次之前,墙裂建议使用conda等工具进行环境隔离
在编译之前,需要安装protobuf,以下是源代码编译安装
git clone https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf.git
cd protobuf
git checkout v5.29.2
git submodule update --init --recursive
mkdir build_source && cd build_source
cmake -Dprotobuf_BUILD_SHARED_LIBS=OFF -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr -Dprotobuf_BUILD_TESTS=OFF -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE=ON ..
cmake --build . --target install
protobuf是一个关键的序列化工具,之后的源代码中的部分.cc和.h文件是由其生成的 然后在主文件夹下使用pip install -e . -v就能编译安装,python 包管理器会将 onnx 关联到当前路径
不过,毕竟需要看代码,所以cmake相关的需要进行一点变动:
- 在
CMakeLists.txt中,加入一行set(CMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS TRUE), 以便生成compile_commands.json, 让clangd作为看c++时的lsp - 使用
cmake -DENABLE_FASTER_BUILD=OFF ., 如果开启快速编译,某些由protobuf生成的文件可能不会保存
在生成的onnx-ml.pb.h中,lsp可能无法解析符号PROTOBUF_NODISCARD, 根据这个commit,应该可以将其替换为编译器自带的[[nodiscard]]
onnx-ml.pb.h会校验c++版本,由于只是需要其提供定义和符号,所以也将其注释
#if PROTOBUF_VERSION != 5029002
#error "Protobuf C++ gencode is built with an incompatible version of"
#error "Protobuf C++ headers/runtime. See"
#error "https://protobuf.dev/support/cross-version-runtime-guarantee/#cpp"
...
...
#endif // ps: 这个endif在文件末尾
最后, 为了进行数据一致性检验,可能需要下一个onnx runtime
ONNX项目组成
由于国内(其实也包括国外),ONNX 的资料不算很多,近年来有些式微,很多训练框架并不愿意全盘兼容ONNX,导致ONNX主打的框架迁移用处不大,然后 ONNX-runtime也不算特别出色。
项目树(仅文件夹):
$ tree onnx -d
├── bin
├── common
├── defs
│ ├── controlflow
│ ├── generator
│ ├── image
│ ├── logical
│ ├── math
│ ├── nn
│ ├── object_detection
│ ├── optional
│ ├── __pycache__
│ ├── quantization
│ ├── reduction
│ ├── rnn
│ ├── sequence
│ ├── tensor
│ ├── text
│ ├── traditionalml
│ └── training
├── frontend
├── inliner
├── onnx_cpp2py_export
├── reference
带.pb的是由protobuf导出的c++文件,带_pb的是导出的python文件
-
bin: 存放了一个checker.py, 方便导出 -
common: c++ 编写的实用程序,如 assert,file,path,platform等, 其中有不少的是Highly Experimental的 -
defs: 存放 ONNX 对于模型各个部件的定义,说实话从技术的角度上没什么好看的 -
frontend: 似乎是空的 -
onnx_cpp2py_export以及onnx_cpp2py_export...so: cpp 和 py 之间进行接口交换 -
reference: 定义了大量的算子,绝大多数是用numpy实现的
ONNX-optimizer
ONNX-optimizer 以 ONNX 作为依赖,配置基本如上所示, 显然更有研究的价值,虽然它的star量大概是其他 AI 编译器的百分之一,贡献者也只有几十人
ONNX-optimizer 使用 ONNX 作为 third-part, 也就是应该首先按照上述方法构建ONNX的环境,否则lsp应该是没法使用的.
首先是文件树:
onnx-optimizer
├── c_api
│ ├── onnxoptimizer_c_api.cc
│ └── onnxoptimizer_c_api.h
├── cpp2py_export.cc
├── __init__.py
├── __main__.py
├── model_util.cc
├── model_util.h
├── onnxoptimizer_main.py
├── optimize.cc
├── optimize.h
├── pass.cc
├── passes
│ ├── adjust_add.h
│ ├── adjust_slice_and_matmul.h
│ ├── bitscast.h
│ ├── cse_util.h
│ ├── data_type.h
│ ├── eliminate_common_subexpression.h
│ ├── eliminate_consecutive_idempotent_ops.h
│ ├── eliminate_deadend.h
│ ├── eliminate_duplicate_initializer.h
│ ├── eliminate_identity.h
│ ├── eliminate_if_with_const_cond.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_cast.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_concat.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_dropout.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_expand.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_flatten.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_monotone_argmax.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_pad.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_reshape.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_split.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_transpose.h
│ ├── eliminate_nop_with_unit.h
│ ├── eliminate_shape_gather.h
│ ├── eliminate_shape_op.h
│ ├── eliminate_slice_after_shape.h
│ ├── eliminate_unused_initializer.h
│ ├── extract_constant_to_initializer.h
│ ├── fuse_add_bias_into_conv.h
│ ├── fuse_bn_into_conv.h
│ ├── fuse_concat_into_reshape.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_concats.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_log_softmax.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_reduce_unsqueeze.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_slices.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_squeezes.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_transposes.h
│ ├── fuse_consecutive_unsqueezes.h
│ ├── fuse_matmul_add_bias_into_gemm.h
│ ├── fuse_pad_into_conv.h
│ ├── fuse_pad_into_pool.h
│ ├── fuse_qkv.h
│ ├── fuse_transpose_into_gemm.h
│ ├── lift_lexical_references.h
│ ├── logging.h
│ ├── nop.h
│ ├── pass_util.cc
│ ├── pass_util.h
│ ├── rename_input_output.h
│ ├── replace_einsum_with_matmul.h
│ ├── rewrite_input_dtype.h
│ ├── set_unique_name_for_nodes.h
│ ├── split.h
│ ├── string_utils.h
│ ├── tensor_util.cc
│ └── tensor_util.h
├── pass.h
├── pass_manager.cc
├── pass_manager.h
├── pass_registry.cc
├── pass_registry.h
└── test
└── optimizer_test.py
可以看出项目比较紧凑(小) 了解构建模式之前,可以先看看给出的使用示例
// onnx_optimizer_exec.cpp
/*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
*/
...
try {
ONNX_NAMESPACE::ModelProto model;
onnx::optimization::loadModel(&model, model_in_path, true);
onnx::checker::check_model(model);
auto new_model = onnx::optimization::Optimize(
model, onnx::optimization::GetFuseAndEliminationPass());
onnx::checker::check_model(new_model);
bool save_external_data = !model_data_path.empty();
onnx::optimization::saveModel(&new_model, model_out_path,
save_external_data, model_data_path);
} catch (std::exception& e) {
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
...
-
ModelProto: 继承于::google::protobuf::Message, 用于模型的存储,修改以及基于protobuf进行序列化, 由ONNX提供 -
loadModel: ONNX-opt提供,当true时,在模型文件同文件夹下寻找并加载额外文件(权重),并调用loadExternalDataForTensor,转化为tensor形式 -
check_model:按照ONNX标准进行检查 -
saveModel: 保存模型和权重 -
onnx::optimization::Optimize/OptimizeFixed: 优化过程分为常规优化和不动点优化,这两个接口将会被导出到python(需安装pybind11)
ONNX-optimizer
ONNX-opt 虽然是一个很古老的 AI 优化器,但可能也有一些参考价值 ONNX-opt 使用 Pass 对模型进行优化,参见源代码onnx-optmizer/pass.h中的 transform pass 的基类
class Pass {
PassType pass_type;
PassEfficiency pass_efficiency;
PassOptimizationType pass_optimization_type;
...
};
// Enum that represents the type of optimization it is.
enum PassType {
// Class of optimizations that fuses operations.
Fuse = 0,
// Class of optimizations that removes useless operations.
Nop = 1,
// Class of optimizations that includes some form of separation.
Separate = 2,
// Immutable pass, also sometimes referred to as an analysis pass.
Immutable = 3,
// Class of optimizations that replaces nodes with other.
Replace = 4,
// Other type of pass.
Other = 5
};
enum PassOptimizationType {
// Is not optimizing anything. Most likely will be used in an immutable pass.
None = 0,
// Optimizes for compute.
Compute = 1,
// Optimizes for memory.
Memory = 2,
// Optimizes for both compute and memory.
ComputeMemory = 3,
// Optimizes for stability (e.g. log-sum-exp trick).
Stability = 4
};
enum PassEfficiency {
// A partially efficient optimization pass cannot guarantee that running two
// consecutive passes
// will return the same result as running a single pass.
Partial = 0,
// A completely efficient optimization guarantees that running two consecutive
// passes is equivalent
// to running a single pass.
Complete = 1
};
transform pass 基于操作类型划分有一下几类
-
Fuse: 进行算子合并 -
Nop: 进行冗余消除 -
Separate:进行算子拆分 -
Immutable: 前后模型不变的pass,有时指代 analysis pass -
Replace: 对计算图节点进行替换 -
Other: 其他 基于pass的效果划分有一下几类 -
None: 无 -
Compute: 改善计算 -
Memory: 改善访存 -
ComputeMemory: … -
Stability: 提高稳定性
最后,一个pass的效果可能是稳定的,也可能是不稳定的
同样,还有analysis pass,定义相对简单, 依赖于上面的Immutable pass,一个 analysis pass 通过 runPass 的返回值获取分析结果
class Pass {
...
virtual std::shared_ptr<PostPassAnalysis> runPass(Graph &graph) = 0;
...
}
// Base struct representing result of a pass.
struct PostPassAnalysis {
virtual ~PostPassAnalysis() = default;
};
// Enum that represents the return type of the analysis.
enum PassAnalysisType {
// An empty analysis is returned. Most likely will return PostPassAnalysis.
Empty = 0,
// A count based analysis is returned. Most likely of type
// CountBasedPassAnalysis
CountBased = 1
};
// Pass Analysis done after a predicate based pass.
struct CountBasedPassAnalysis : PostPassAnalysis {
Pass *pass;
...
bool graphChanged();
bool numSucceededTransforms();
...
// Whether or not a repeated application of the pass might be useful.
bool fixedPointOptimizationNeeded() {
return this->graphChanged() &&
pass->getPassEfficiency() == PassEfficiency::Partial;
}
...
};
CountBasedPassAnalysis应该是目前ONNX-opt唯一的PostPassAnalysis的继承示例(empty无需继承)
Pass *pass 是 runPass 中传入的 this 指针
PassManager
ONNX-opt 有两类Manager可用,对应上一节提到的两种Optimizer, 一种是GeneralPassManager,另一种是FixedPointPassManager
class PassManager {
...
};
class GeneralPassManager : public PassManager {
public:
GeneralPassManager() {}
~GeneralPassManager() override;
void add(std::shared_ptr<Pass> pass) override;
std::shared_ptr<PassManagerAnalysis> run(Graph& graph) override;
protected:
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Pass>> passes;
};
class FixedPointPassManager : public GeneralPassManager {
std::shared_ptr<PassManagerAnalysis> run(Graph& graph) override;
};
没有任何理解上的难度,下面是如何实现这么一个 fix point:
std::shared_ptr<PassManagerAnalysis> FixedPointPassManager::run(Graph& graph) {
bool fixed_point_optimization_done;
do {
fixed_point_optimization_done = false;
for (const std::shared_ptr<Pass>& pass : this->passes) {
std::shared_ptr<PostPassAnalysis> analysis = pass->runPass(graph);
if (pass->getPassAnalysisType() == PassAnalysisType::Empty) {
continue;
}
std::shared_ptr<CountBasedPassAnalysis> count_analysis =
std::static_pointer_cast<CountBasedPassAnalysis>(analysis);
while (count_analysis->fixedPointOptimizationNeeded()) {
count_analysis = std::static_pointer_cast<CountBasedPassAnalysis>(
pass->runPass(graph));
fixed_point_optimization_done = true;
}
}
} while (fixed_point_optimization_done);
return std::shared_ptr<PassManagerAnalysis>(new EmptyPassManagerAnalysis());
}
也是非常简单,当runPass返回的 analysis 结果不为空时,调用fixedPointOptimizationNeeded检查是否可以进行不动点迭代,然后一直迭代到没有不同点为止
两类 transform pass
PredicateBasedPass
基于计算图上匹配字图的 transform pass,有两个关键方法patternMatchPredicate和runTransform, 在实际进行pass之前,先使用前者匹配字图, 如果匹配到则调用后者进行转换,这个流程在 runPass -> _runPassInternal 执行。ONNX-opt 的大部分的 pass 都是这种类型
class PredicateBasedPass : public Pass {
public:
explicit PredicateBasedPass(PassType pass_type,
PassEfficiency pass_efficiency,
PassOptimizationType pass_optimization_type)
: Pass(pass_type, pass_efficiency, pass_optimization_type) {}
~PredicateBasedPass() override;
virtual bool patternMatchPredicate(Node *node) = 0;
virtual bool runTransform(Node *node, Graph &graph,
NodeDestroyType &destroy_current) = 0;
std::shared_ptr<PostPassAnalysis> runPass(Graph &graph) override;
PassAnalysisType getPassAnalysisType() const override;
static int getOpsetVersion(const Graph &g) {
Graph &mut_g = const_cast<Graph &>(g);
for (const OpSetID &opset : mut_g.opset_versions_mutable()) {
if (opset.domain() == "") {
return opset.version();
}
}
return 0;
}
private:
unsigned int _runPassInternal(Graph &graph);
};
这里比较重要的是 runTransform 是如何修改图的,这个需要之后对 ONNX 的 IR, Node, Graph 等内容进行分析
FullGraphBasedPass
在图上的优化:
// The most general pass which allows the user to run a pass given only a graph.
class FullGraphBasedPass : public Pass {
public:
explicit FullGraphBasedPass(PassType pass_type,
PassEfficiency pass_efficiency,
PassOptimizationType pass_optimization_type)
: Pass(pass_type, pass_efficiency, pass_optimization_type) {}
~FullGraphBasedPass() override;
};
举个例子,eliminate_deadend.h, 大致就是在计算图上,根据use关系,找到 unreachable node 并删除的优化
unsigned int EliminateDead(Graph& graph) {
unsigned int nodes_removed = 0;
auto nodes = graph.nodes().reverse();
for (auto it = nodes.begin(); it != nodes.end(); it++) {
auto node = *it;
if (!node->hasUses()) {
nodes_removed++;
it.destroyCurrent();
}
}
return nodes_removed;
}
可以看到,nodes 是图中节点的拓扑排序
ONNX IR
位于源文件 onnx/ir.h, 有三个关键结构 Value, Node, Graph
// Graph represents one "function" of computation.
// It uses a simple ownership model where the graph owns all the nodes inside it.
// All references inside the graph are raw pointers.
// Destroying the Graph will invalidate any pointers to nodes in the graph.
struct Graph;
// Node is the base class of the IR graph. It represents one computation
// and dependencies on a list of Values. The "prim-ops", so to speak.
struct Node;
// A Value represents an input or output to node that is either a
// Tensor or an opaque Handle object, as determined by type().
struct Value;
Value 持有定义本身的 Node 的引用,即一个 Value 是一个 Node 的 output 之一,即 use-def关系中的 def关系
struct Value final {
Node* node_;
size_t offset_;
size_t unique_ = 0; // unique id
size_t stage_ = 0; // 0-forward, 1-backward, 2-double-backward,...
use_list uses_in_current_graph_;
bool has_unique_name_{false};
std::string unique_name_;
int32_t elem_type_{ONNX_NAMESPACE::TensorProto_DataType_UNDEFINED};
bool has_sizes_{false};
std::vector<Dimension> sizes_;
...
};
Node 代表的是计算图中的实际的或者虚拟的节点,也是 Graph 中由拓扑序构成的双向链表的节点,在进行opt时,需要维护双向链表以及其代表的拓扑排序
同时,Node 引用 inputs_ 作为节点的 operands, 持有 outputs_ 作为 def
struct Node : public Attributes<Node> {
...
std::array<Node*, 2> next_in_graph{nullptr, nullptr};
Node*& next();
Node*& prev();
...
std::vector<Value*> inputs_;
std::vector<Value*> outputs_;
Graph* graph_;
size_t stage_;
...
};
Graph 代表的是 function 的角色,并持有其中所有 Node 的内存
那么什么是function? 在这里,function 是一个计算机科学概念,指的是一个拥有明确输入和输出的、自包含的计算单元
-
all_nodesall_values用于管理内存 -
output_: 作为 ret 虚拟节点,其inputs_为该图的输出 -
input_: 作为 params 虚拟节点,其outputs_为该图的输入 -
initializers_: 权重初始化器,包含该 function 中会用到的常量
不难看出,Graph 本身并不直接管理 Node 链表
理论上说,function 和 graph 的概念是不同的,他们的划分依据并不相同。function 一般依照功能性进行划分,而 graph 的划分依据一般是算子本身的语义需求,比如带控制流的算子
struct Graph final {
...
std::unordered_set<const Node*> all_nodes;
std::unordered_set<const Value*> all_values;
...
Node* const output_;
Node* const input_;
...
Node* const initializer_node_;
// Create an independent node list for those initializers do not exist in input
std::vector<Tensor> initializers_;
std::vector<std::string> initializer_names_;
...
};
ONNX IR 的组织模式和传统编译器十分甚至九分的相似:function, value, def-use 等概念. 现在还有最后一块拼图,value 如何反向引用到其uses
inline use_list Value::uses() const {
use_list all_uses = uses_in_current_graph_;
owningGraph()->forEachNode([this, &all_uses](const Node* node) {
if (node->owningGraph() == this->owningGraph()) {
// skip non-subgraph
return;
}
if (node->kind() == kCaptured) {
const Value* output = node->outputs()[0];
if (output->uniqueName() == this->uniqueName()) {
const auto output_uses = output->uses();
all_uses.insert(all_uses.end(), output_uses.begin(), output_uses.end());
}
}
});
return all_uses;
}
uses_in_current_graph_ 是一个在 Value 中的缓存,每当 Value 本身需要添加 inputs 时,被添加的 Value 就会更新该缓存,不过该缓存仅在当前子图中生效
Value 显式查找 use_list 时,在同一个子图中则跳过,并当 node->kind() 为 kCaptured 时,递归查找该 node 的 use_list 并添加
可以看出这里的uses() 查找是跨 Graph 也即跨 function 的查找,并且包含直接或者间接的所有 uses (不过理论复杂度直接爆炸)
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: